The platform has a high frequency ultrasound machine (Vevo 3100) specifically manufactured for use in mice and rats. This system was developed by VisualSonics in Toronto, Canada. The probes range from 30 to 50 MHz with very shallow focal lengths, allowing excellent visualization (around 30 microns).All non-invasive ultrasound are performed under light general isoflurane anesthesia.
Ultrasound Imaging
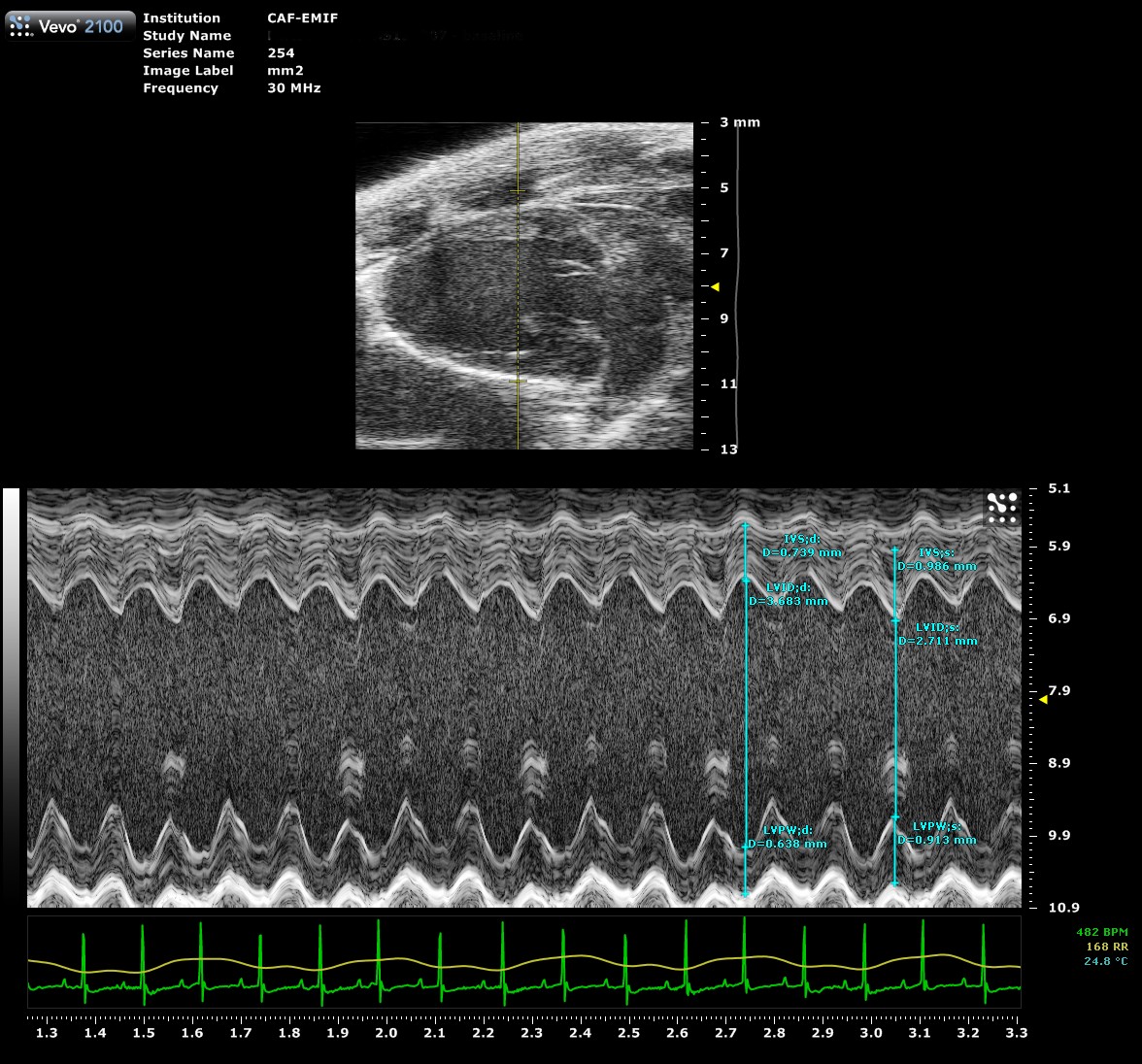
| Cardiac dimensions and function
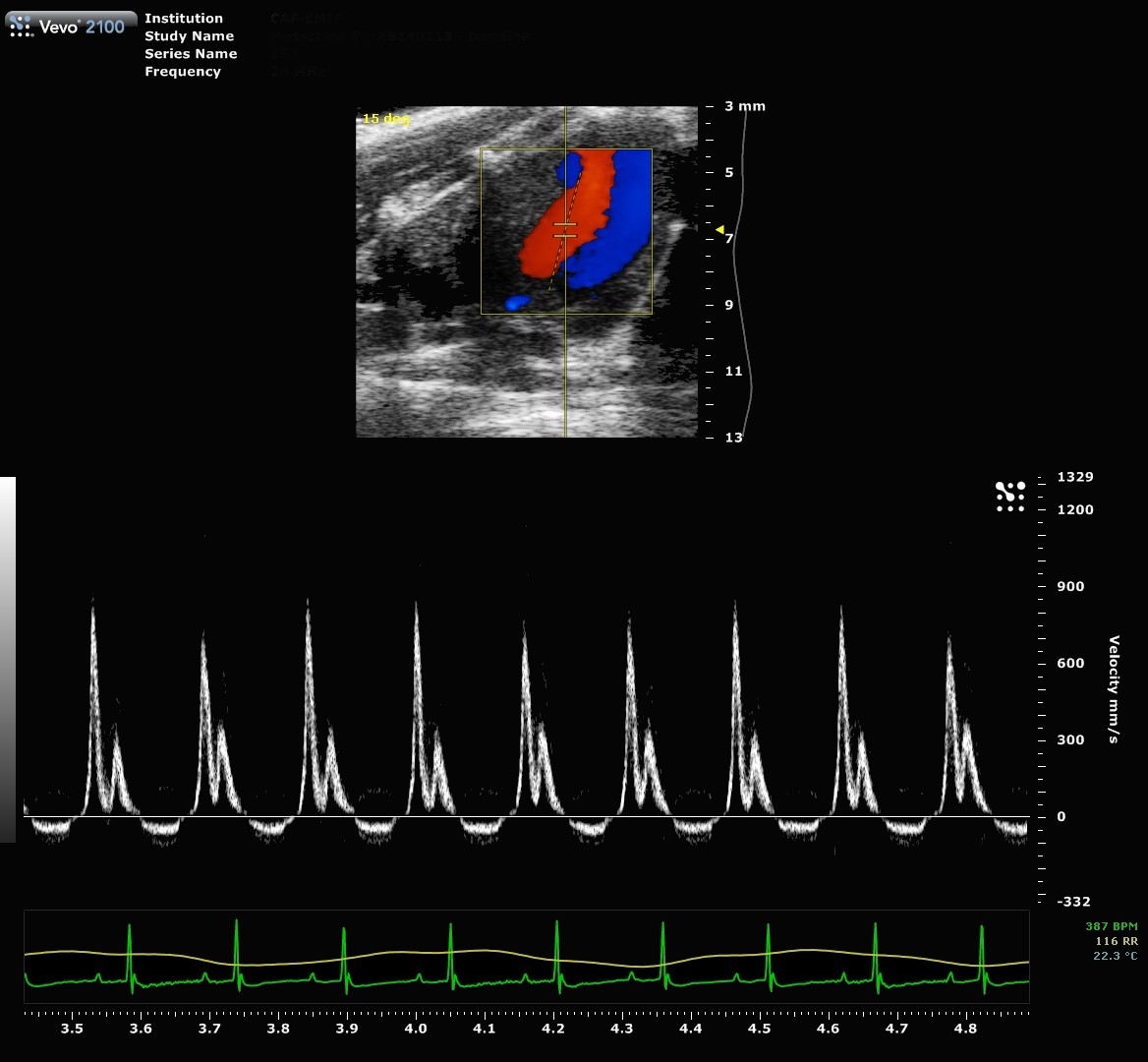
| Pulse-wave Doppler
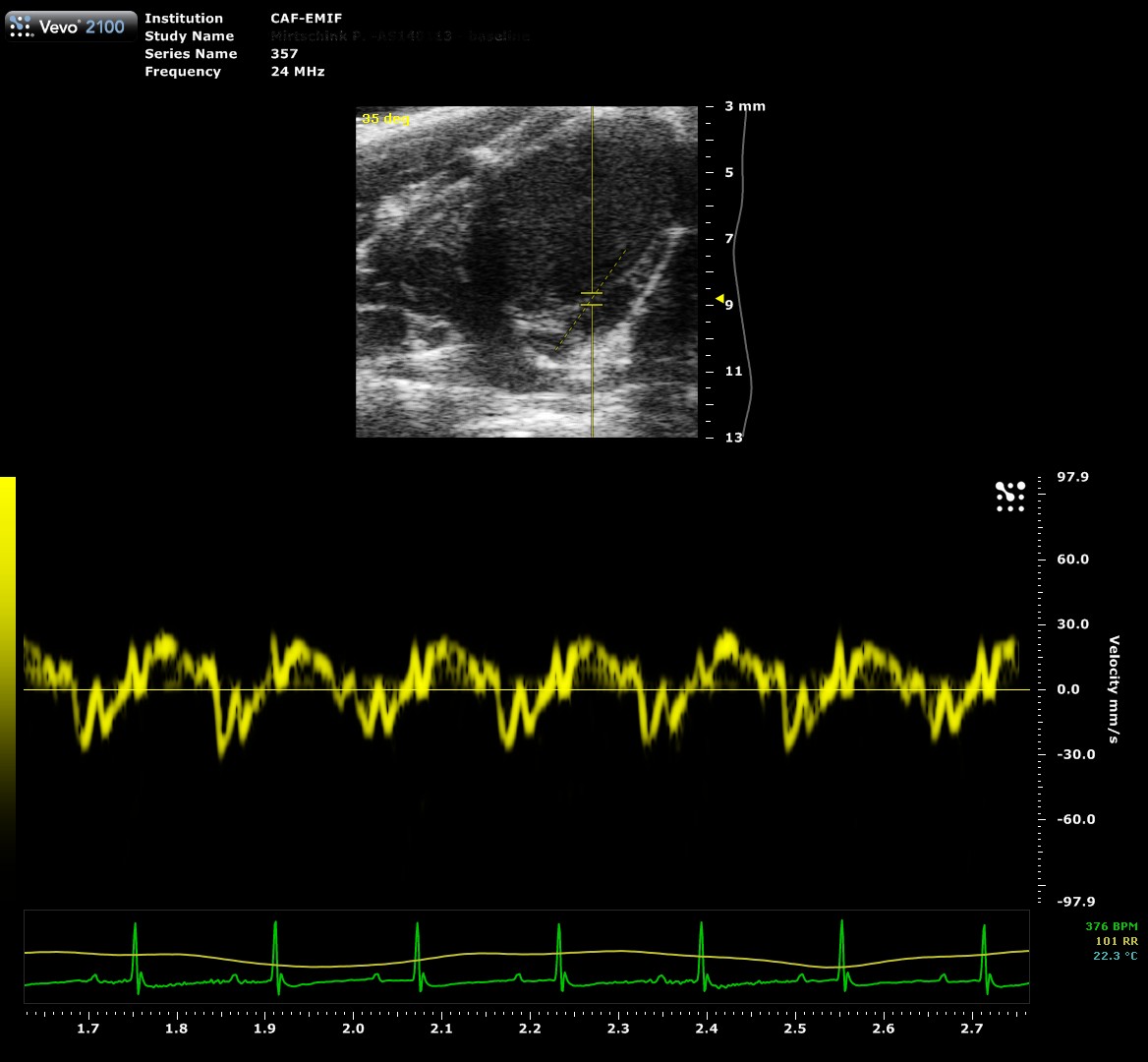
| Speckle-tracking
| Vascular wall motion analysis
| Oncology / tumor growing
| Image-guided injection
| Other features
Cardiac dimensions and function
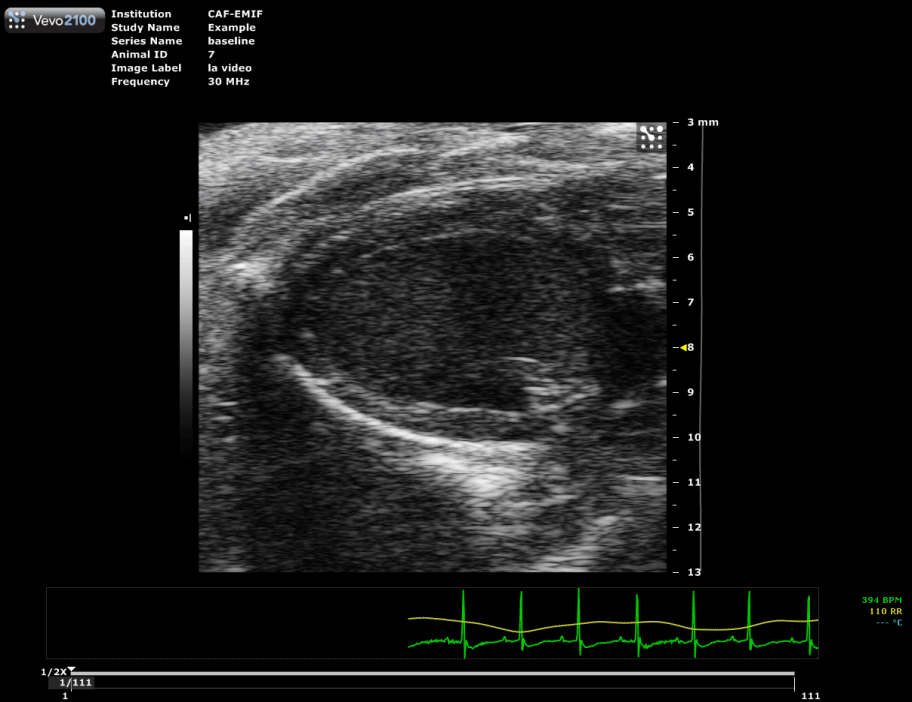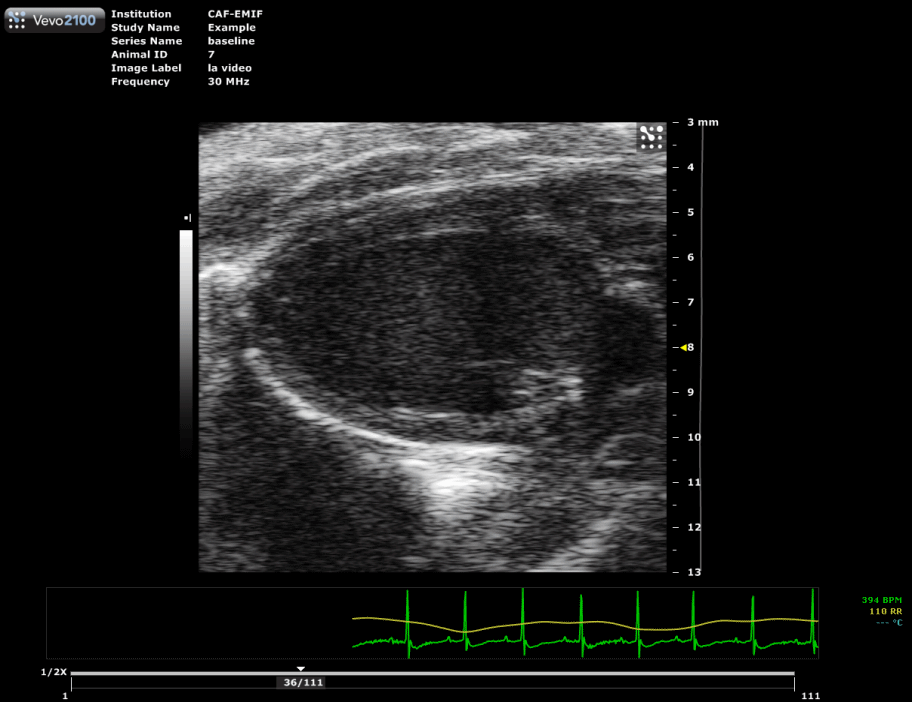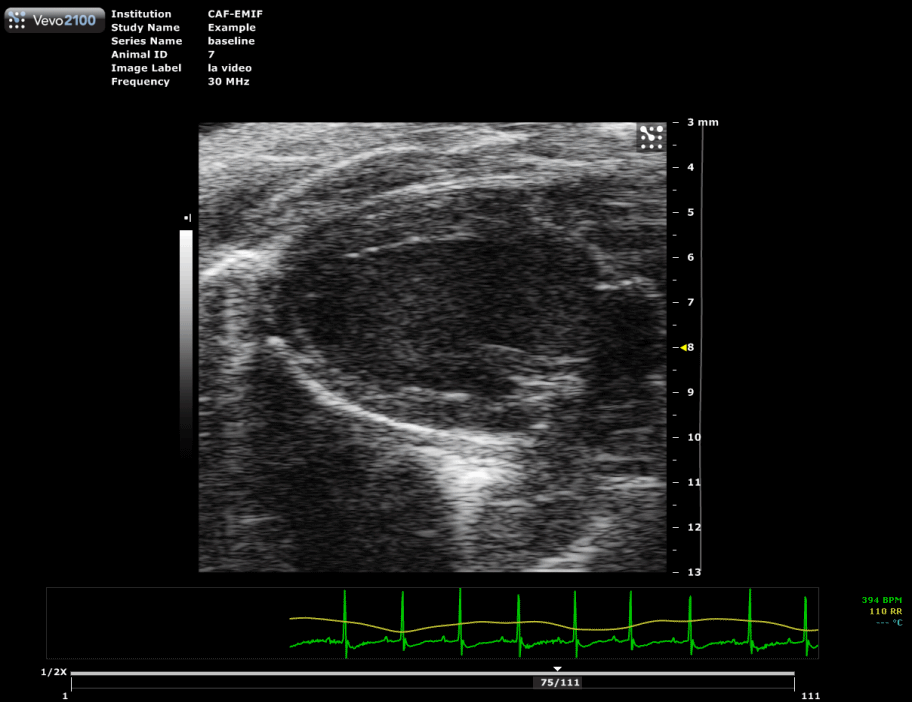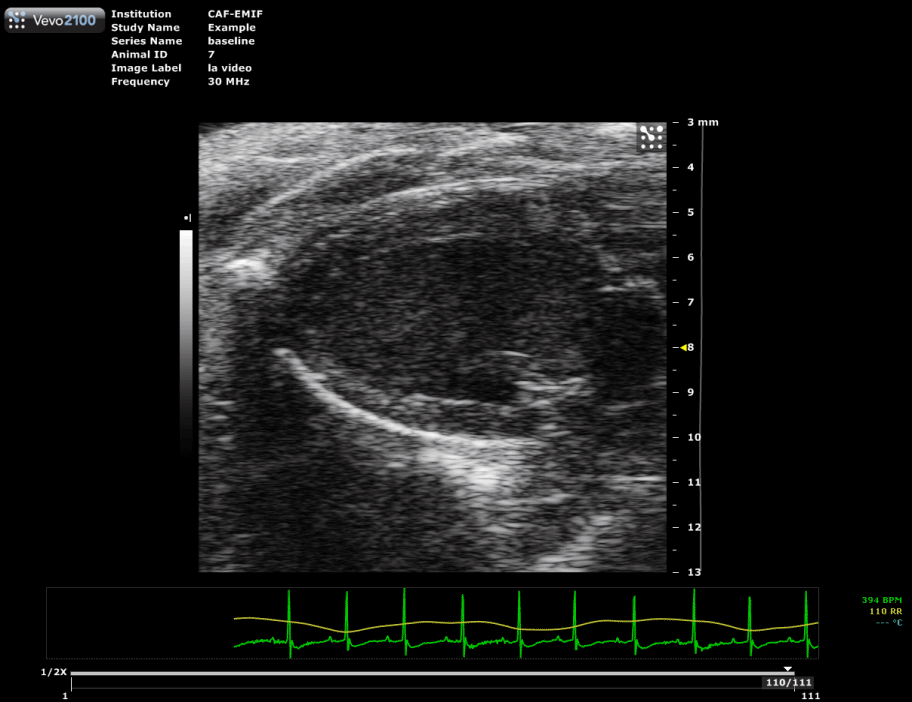
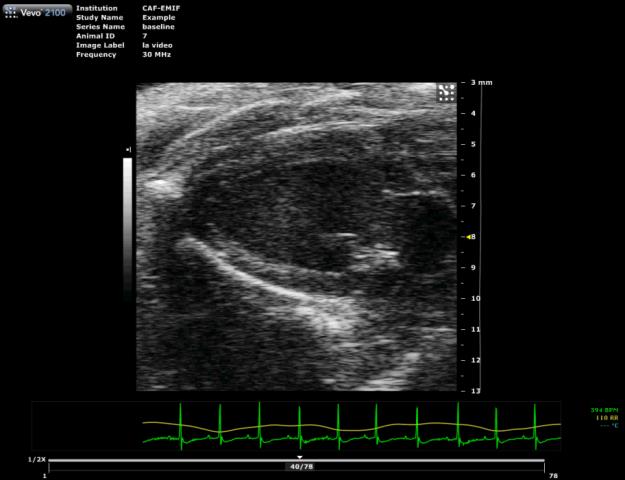
Long axis view of a mouse heart
Pulse-wave Doppler
Speckle-tracking
Speckle-traking imaging is non-Doppler-based technique used to detect myocardial wall motion (velocity, displacement) and myocardial deformation (strain and strain rate).
With the use of VevoStrain software, a value can be obtained which quantifies the velocity, the displacement, the strain and strain rate that is experienced by the selected area of myocardium. It allows for the comparison of one or several points along the left ventricule in parasternal long or short axis.
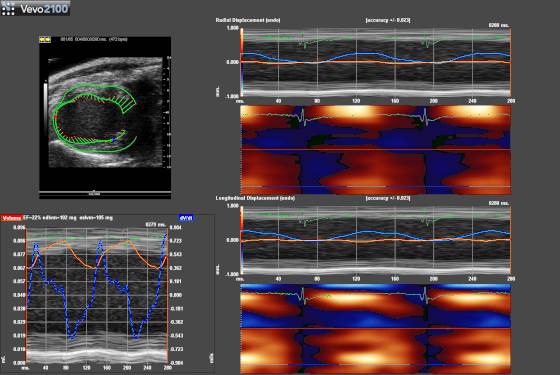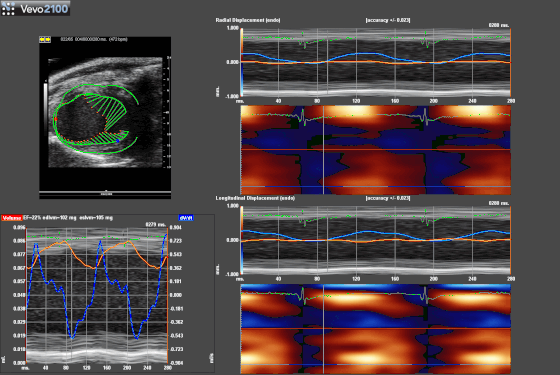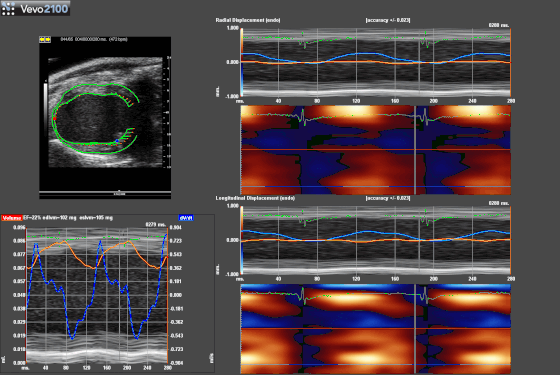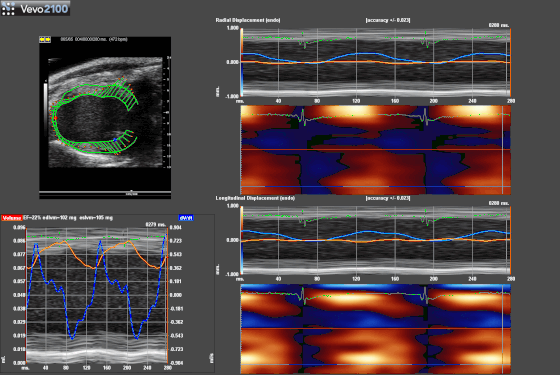 |
| Exemple of Speckle-traking in an infarcted heart. |
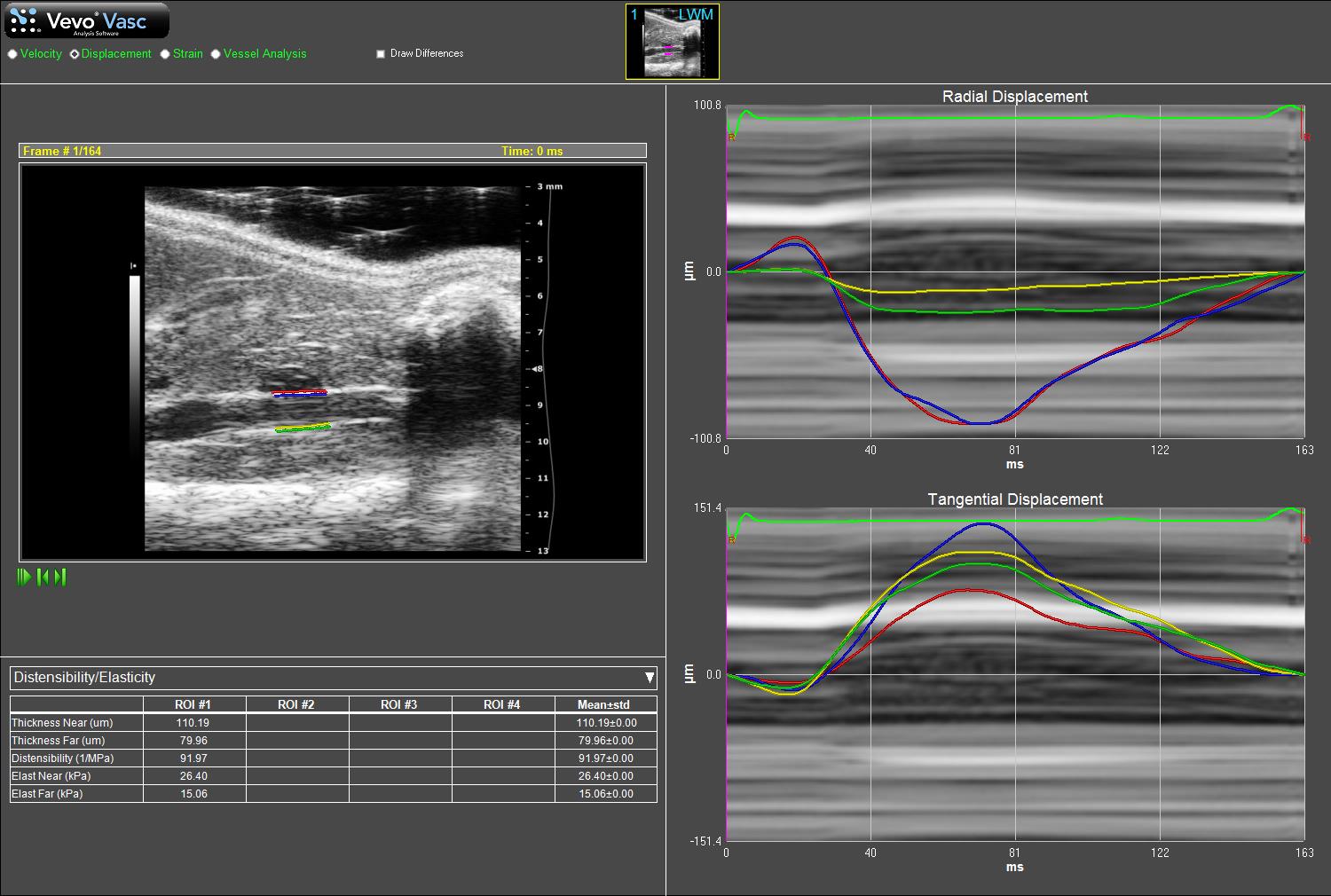
Vascular wall motion analysis
VevoVasc Analysis Software is a vascular strain analysis package that utilizes advanced speckle tracking algorithms on high-resolution ultrasound data to quantify vascular pathologies non-invasively and in vivo.
The software includes both qualitative and quantitative tools to study various vascular disease models.
1) Vessel Wall Tracking.
2) Vessel Stiffness Quantification Using Pulse Propagation Velocity.
3) Vessel Wall Analysis and Micro-Anatomy.
Oncology / tumor growing
CAF also offers monitoring of tumor growth by ultrasound. This non-invasive technique allows a regular and precise follow-up of the growth of tumoral masses. Imaging is performed under light anesthesia (isoflurane) and the volume of the tumor can be regularly calculated and followed.
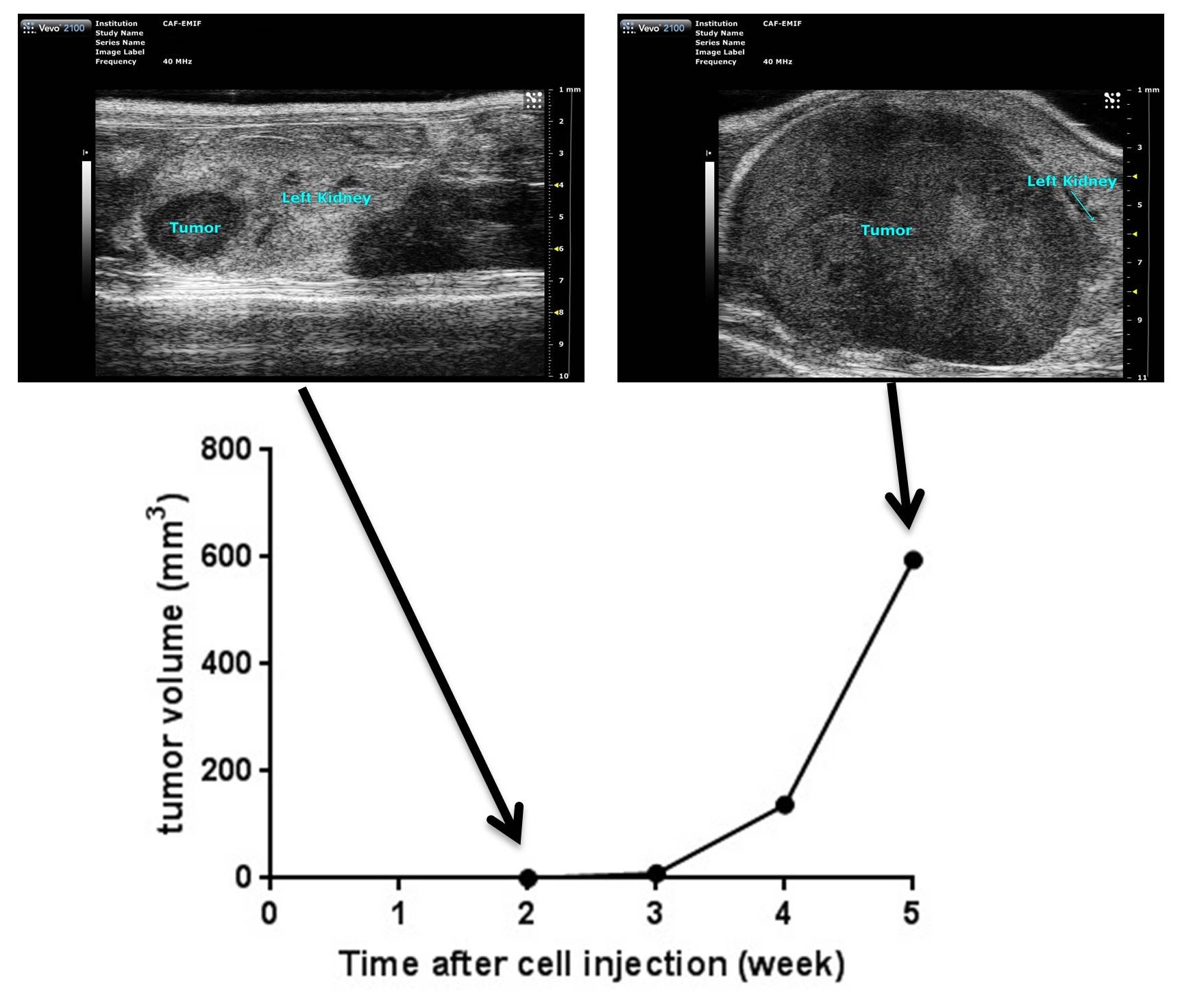
The tumor can be illustrated by a three-dimensional reconstruction:
.jpg)
3D-reconstruction of a tumor (blue) into the kidney (red). (Cornaz-Buros et al ; 2014)
Image-guided injection
Ultrasound-guided injection allows administration of drug or cells into a tissue (near the skin) under anaesthesia.

Image-guided injection into a tumor

Image-guided injection into the left ventricle of a mouse heart
Other features
Visualization of embryos in utero, neonatal echography, and abdominal ultrasound can also be performed. The system is also equipped with Power Doppler technology and 3D analysis.
 |
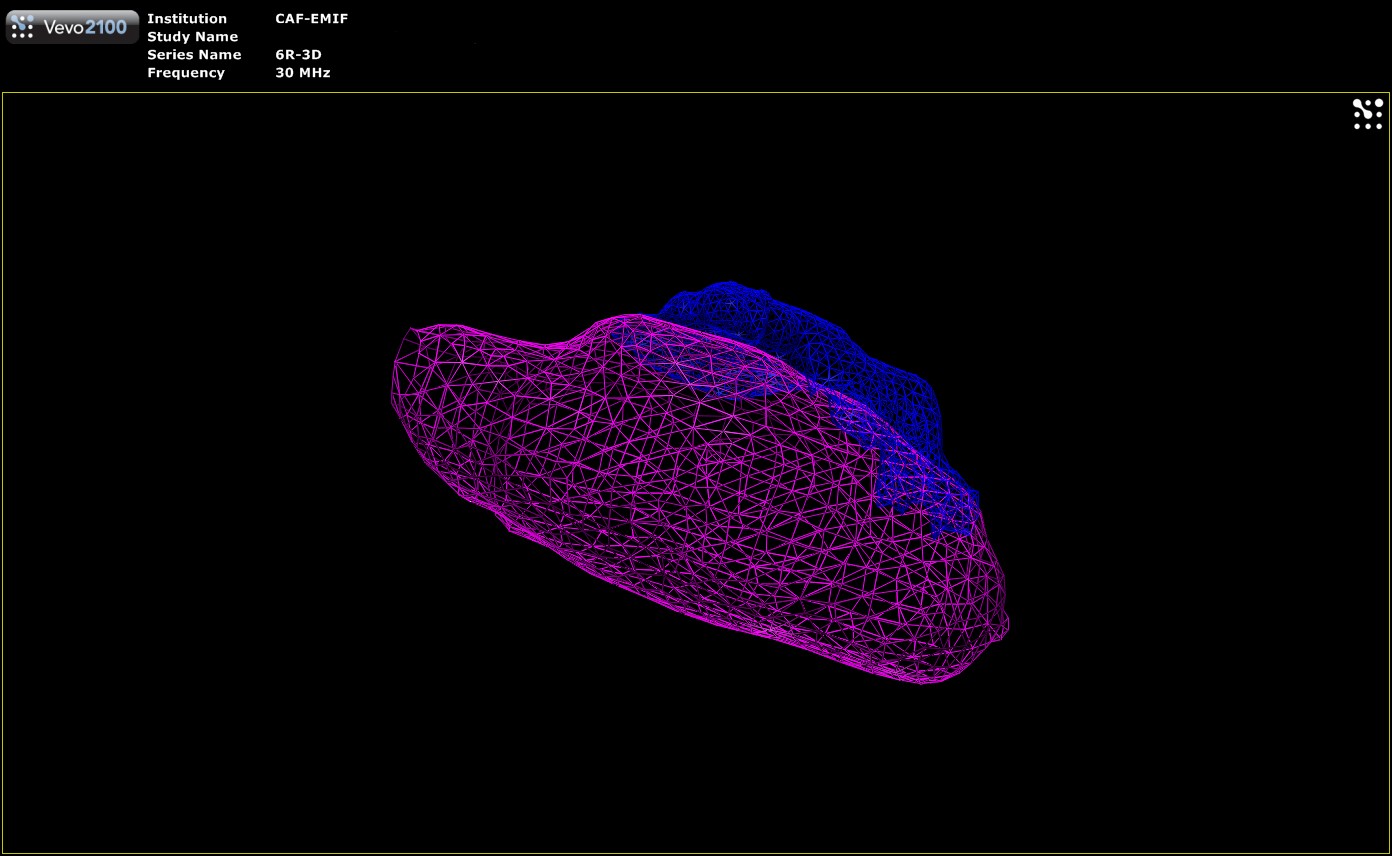 |
| 11-day-old rat embryo | 3D volume reconstruction of a tumor (blue) into a kidney (pink) |