These techniques can be performed in rat and mice.
Microsurgery (pathophysiological models)
| Models of hypertension
| Myocardial Infarction (MI)
| Myocardial infarction in newborn mice
| Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Model
| Model of hypertrophy
| Other models
Models of hypertension
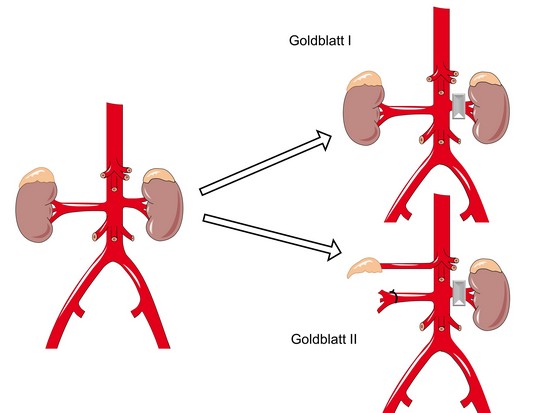
Goldblatt I (2K1C) and Goldblatt II (1K1C)
A left lateral abdominal incision is used to expose the kidney. A clip is placed around the left renal artery (Goldblatt I and II) in order to reduce the renal blood flow. For the Goldblatt II method, a right-nephrectomy is also performed.
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
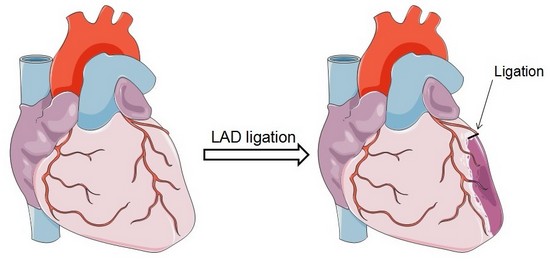
Ligation of left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery
A left lateral thoracotomy is performed on anesthetized and ventilated animal to expose the heart. A ligature near the insertion of the left auricular appendage is placed and tied around the left descending coronary artery. Occlusion of the artery is verified by the rapid blanching of the left ventricle. The ends of the occluding ligature are trimmed and the chest and skin incision are closed.
 |
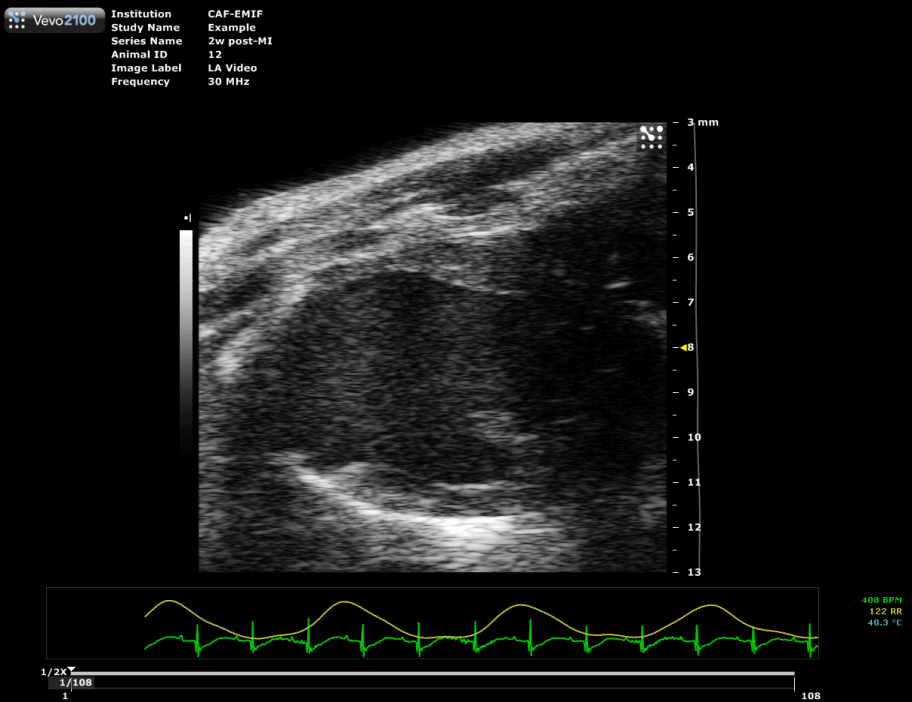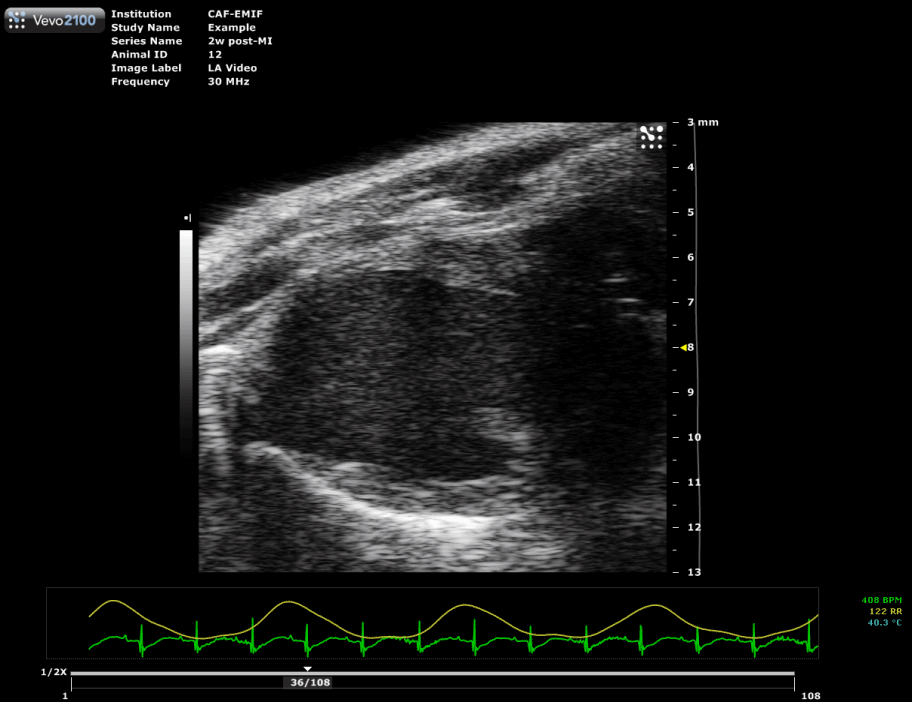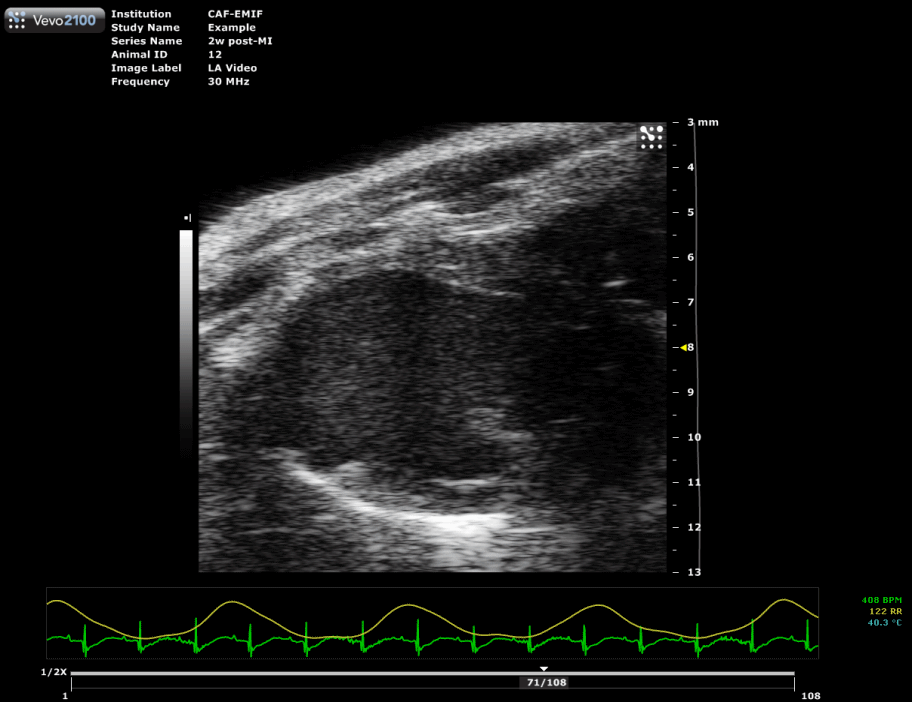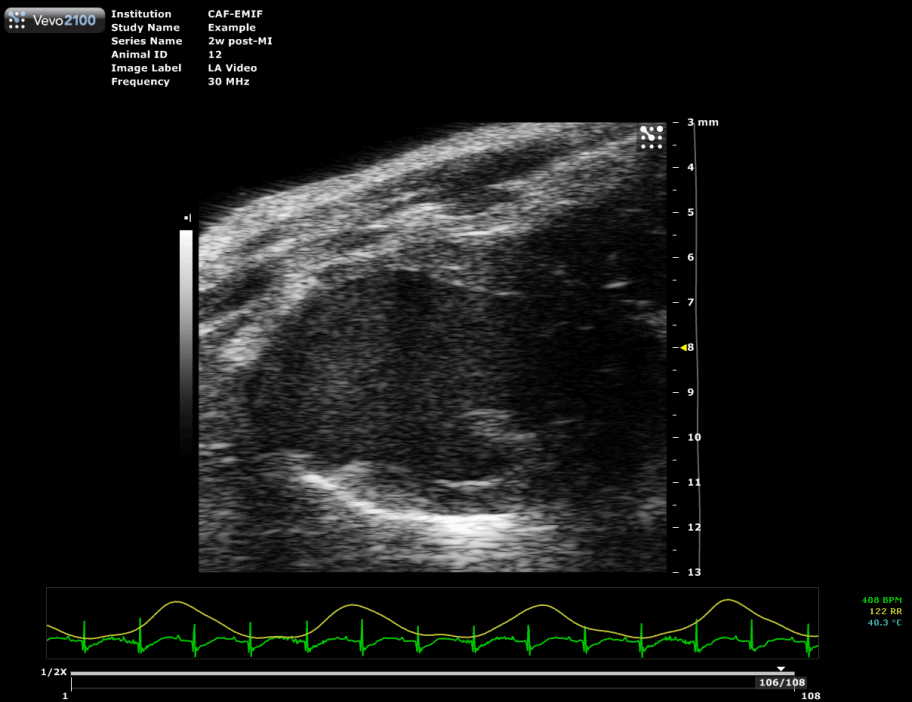 |
| Mouse heart with infarction |
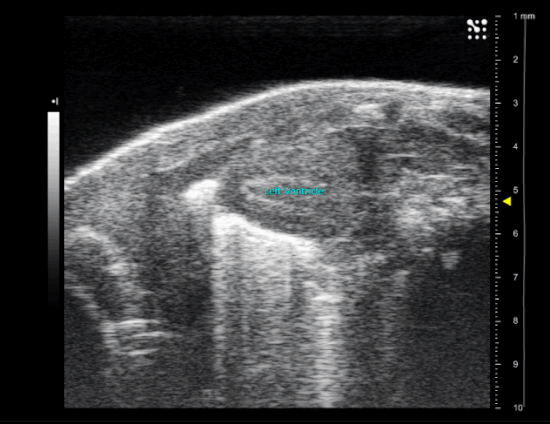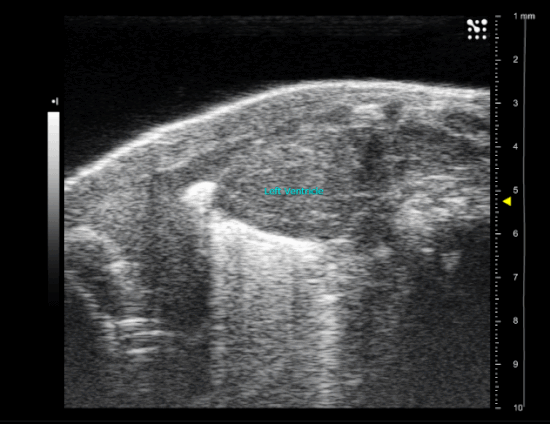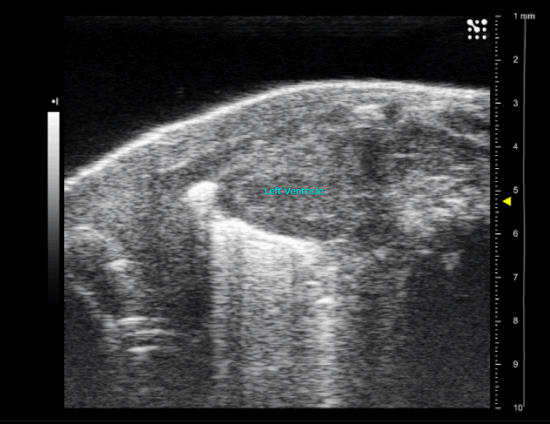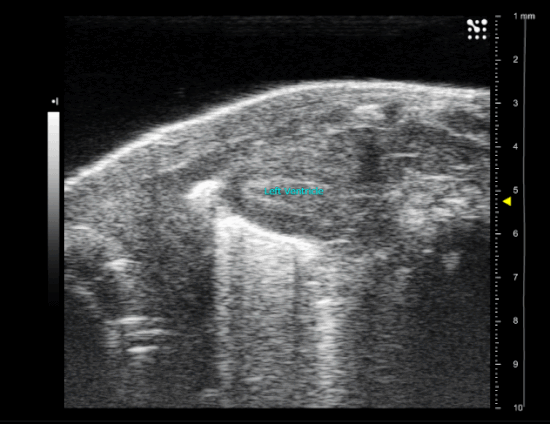
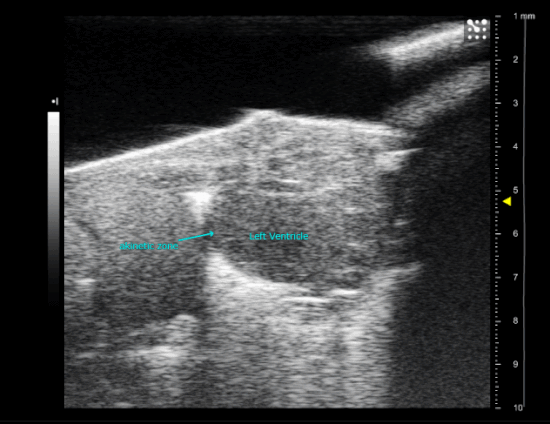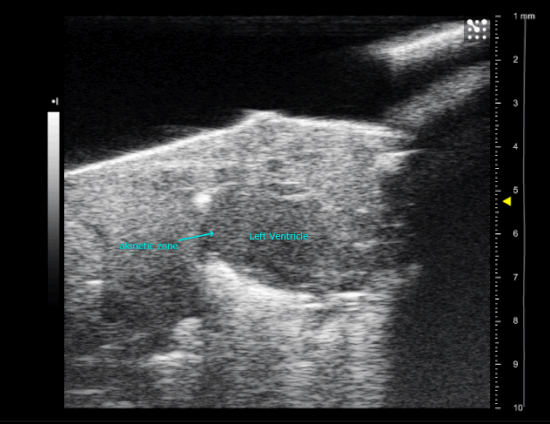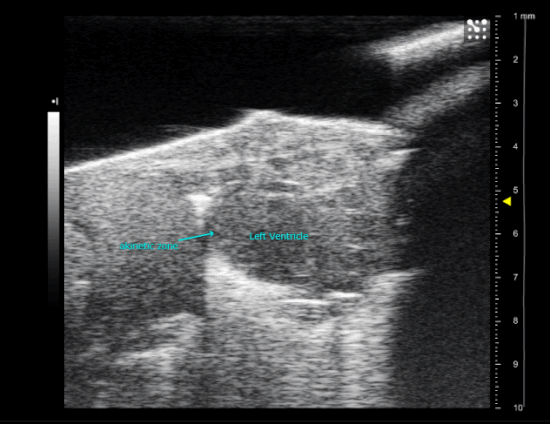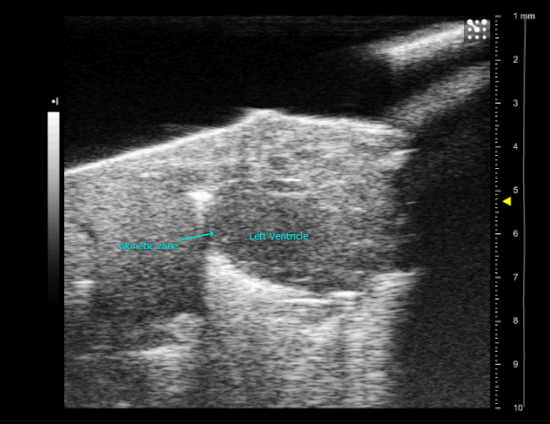
Myocardial infarction in newborn mice
CAF offers the myocardial infarction model in newborn mice.
As for adult, a left lateral thoracotomy is performed on anesthetized animal to expose the heart. A ligature near the insertion of the left auricular appendage is placed and tied around the left descending coronary artery. The ends of the occluding ligature are trimmed and the chest and skin incision are closed.
 |
|
sham operated new born mice heart (P1)
|
 |
|
Myocardial Infarction in a new-born mice heart, operated at P1
|
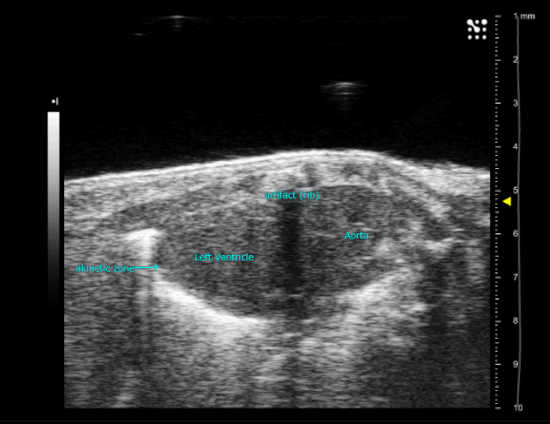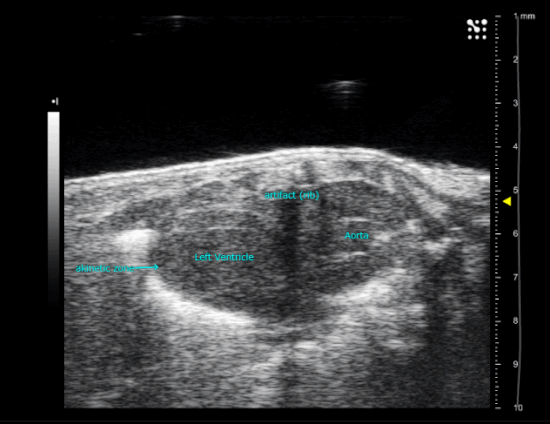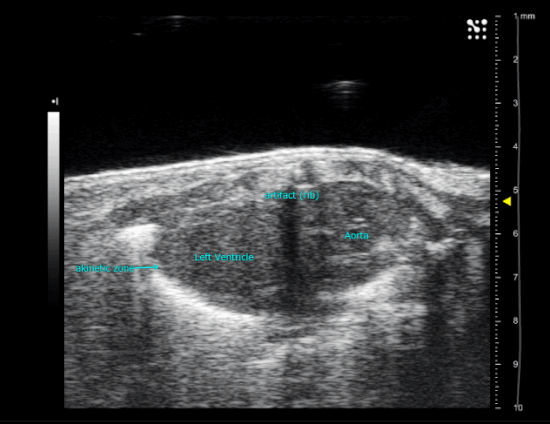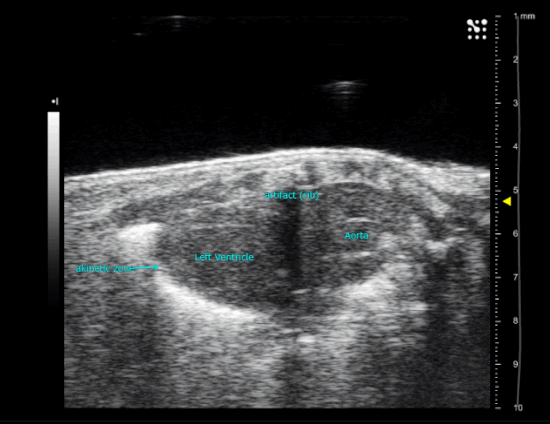 |
| Myocardial Infarction in a new-born mice heart, operated at P3 |
Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Model
For ischemia/reperfusion studies, the procedure is identical to the MI procedure, however the ligature is left in place for a predetermined amount of time (normally 30 to 60 minutes), and then removed prior to chest closure.
Model of hypertrophy
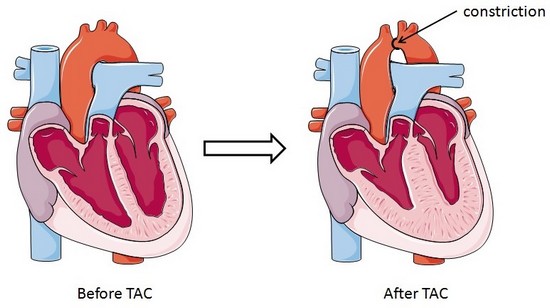
Trans-aortic constriction (TAC)-induced pressure overload
A small horizontal incision is made at the level of the cranial sternum allowing visualization of the aortic arch. A suture is placed around the aorta between the origin of the right innominate and left common carotid artery. Transaortic constriction (TAC) is created using a suture tied twice around the aorta and a predetermined-gauge needle size. The needle is then gently retracted and the incision closed.
 |
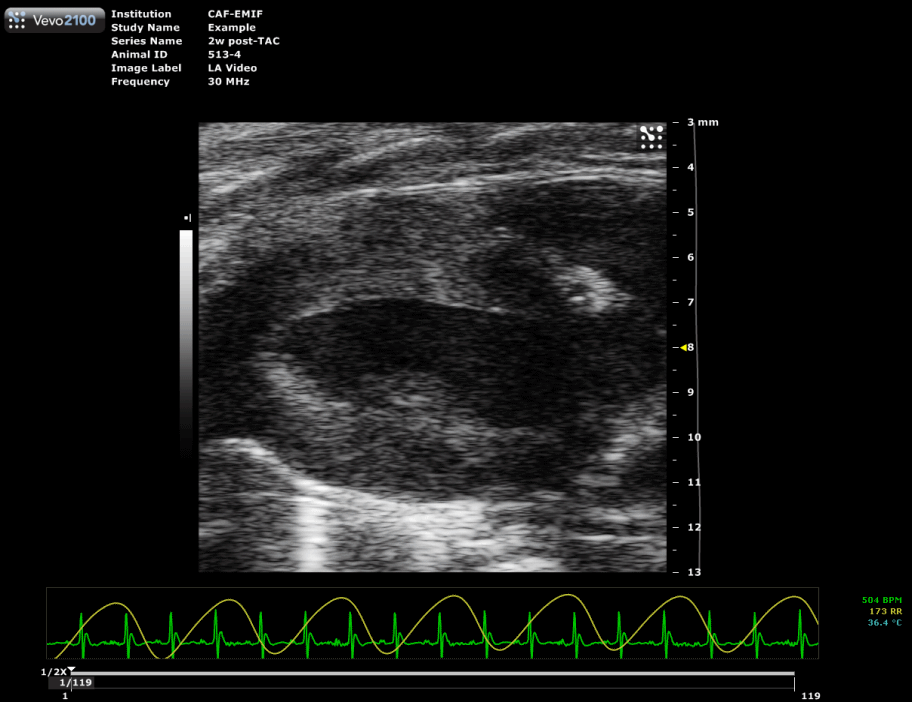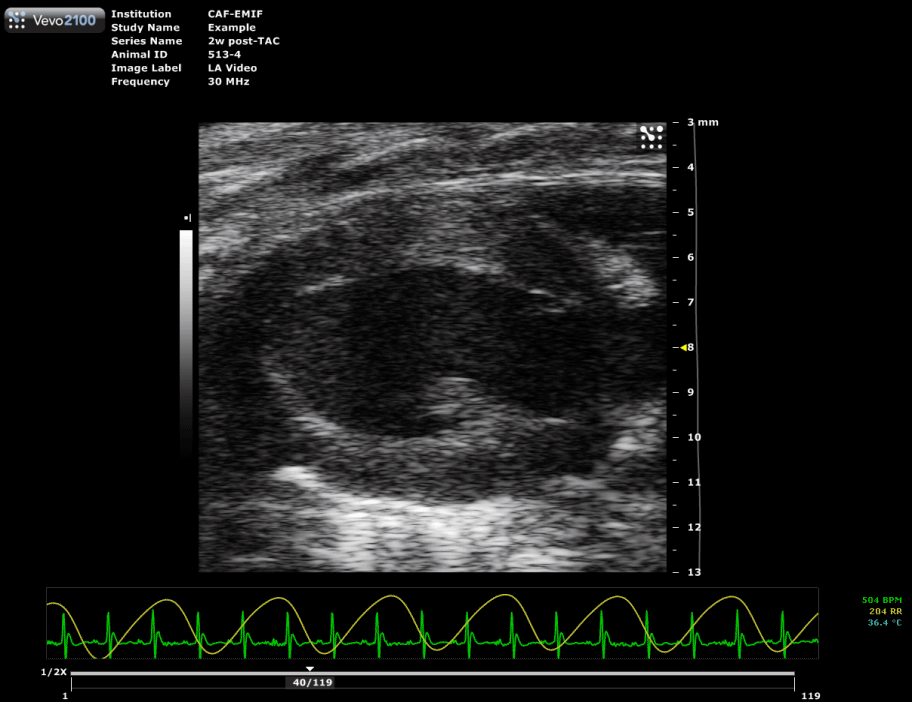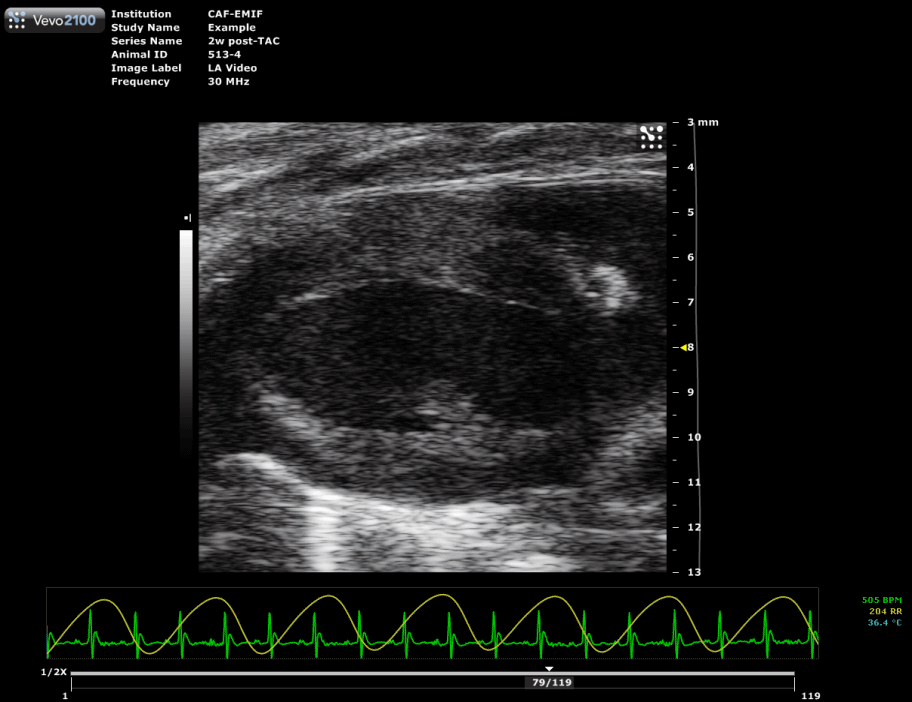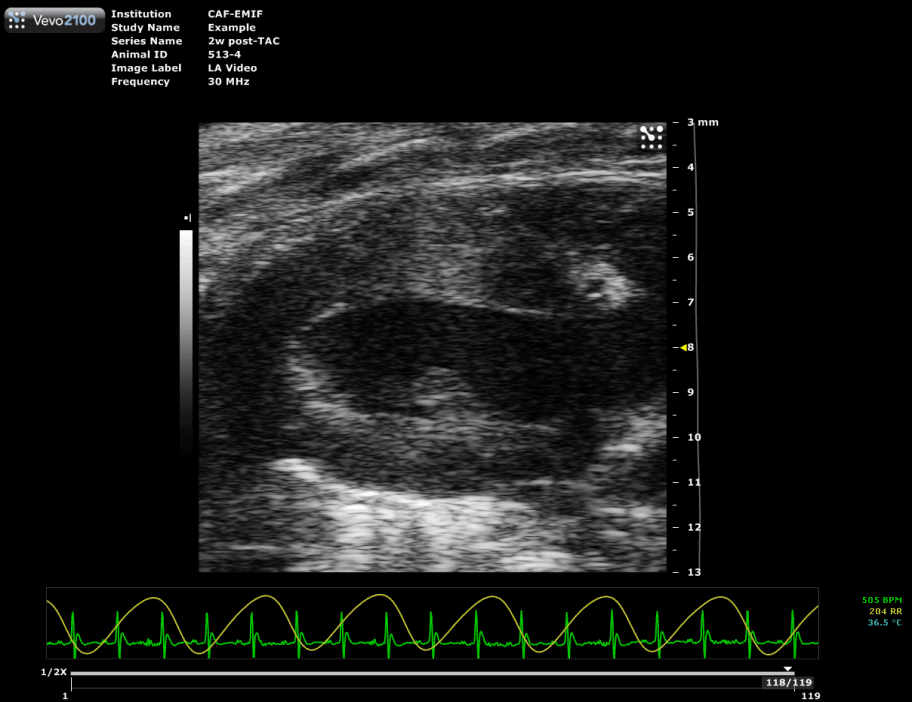 |
| Hypertrophied mouse heart two weeks after TAC surgery. |

